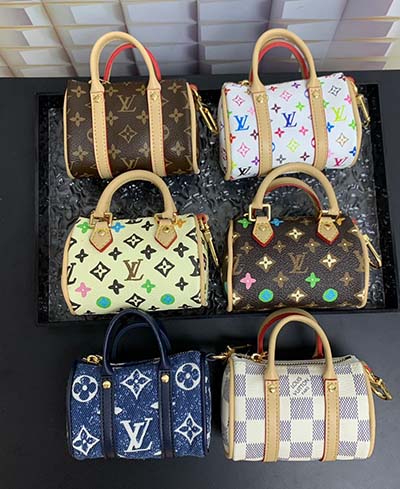
lv raid | raid levels jbod lv raid How blocks of data in an LV are placed onto physical devices is determined by the RAID level. . All Louis Vuitton belts have an identification number on the backside. This identification number defines the style of the belt. Two numbers below indicate the size in centimeters and inches and can vary. Read more on Louis Vuitton belt sizes her. Note that some vintage belts don't have any serial numbers.
0 · raid z1 vs z2 z3
1 · raid levels minecraft
2 · raid levels jbod
3 · raid levels explained
4 · raid levels diagram
5 · raid levels chart
6 · raid explained for dummies
7 · raid 5 6 or 10
The LV Iconic 20 mm reversible belt features the House's Damier Azur canvas on one side and smooth calf leather on the other. The belt buckle shows off the LV Initials in gleaming hardware. This accessory coordinates with a bucket hat from the same collection and with many pieces from the Ready-to-Wear collection.
How blocks of data in an LV are placed onto physical devices is determined by the RAID level. .
When you create a RAID logical volume (LV), LVM creates a metadata subvolume that is one .
raid z1 vs z2 z3
raid levels minecraft
How LV data blocks are placed onto PVs is determined by the RAID level. RAID levels are . LVM supports Raid takeover, which means converting a RAID logical volume .How LV data blocks are placed onto PVs is determined by the RAID level. RAID levels are . To create a RAID logical volume, you specify a raid type as the --type argument .
LVM RAID is a way to create a Logical Volume (LV) that uses multiple physical devices to .There is a huge benefit in having LV based RAID. I do have a LV with RAID1 for more hard to .How blocks of data in an LV are placed onto physical devices is determined by the RAID level. RAID levels are commonly referred to by number, e.g. raid1, raid5. Selecting a RAID level involves tradeoffs among physical device requirements, fault tolerance, and performance.When you create a RAID logical volume (LV), LVM creates a metadata subvolume that is one extent in size for every data or parity subvolume in the array. For example, creating a 2-way RAID1 array results in two metadata subvolumes (lv_rmeta_0 and lv_rmeta_1) and two data subvolumes (lv_rimage_0 and lv_rimage_1).
How LV data blocks are placed onto PVs is determined by the RAID level. RAID levels are commonly referred to as 'raid' followed by a number, e.g. raid1, raid5 or raid6. Selecting a RAID level involves making tradeoffs among: physical device . LVM supports Raid takeover, which means converting a RAID logical volume from one RAID level to another (such as from RAID 5 to RAID 6). Changing the RAID level is usually done to increase or decrease resilience to device failures or to restripe logical volumes. You use the lvconvert for RAID takeover.How LV data blocks are placed onto PVs is determined by the RAID level. RAID levels are commonly referred to as ’raid’ followed by a number, e.g. raid1, raid5 or raid6. Selecting a RAID level involves making tradeoffs among: physical device requirements, fault tolerance, and performance. A description of the RAID levels can be found at
To create a RAID logical volume, you specify a raid type as the --type argument of the lvcreate command.LVM RAID is a way to create a Logical Volume (LV) that uses multiple physical devices to improve performance or tolerate device failures. In LVM, the physical devices are Physical Volumes (PVs) in a single Volume Group (VG).There is a huge benefit in having LV based RAID. I do have a LV with RAID1 for more hard to reproduce data and normal LVs for the rest, this gives me maximum flexibility for size vs. redundancy considerations.
LVM RAID is a method to create a logical volume (LV) which uses several physical disks to improve performance or fault tolerance. Within LVM, physical disks (abbreviated as PV, physical volumes) belong to one volume group (VG).This article will provide an example of how to install and configure Arch Linux with Logical Volume Manager (LVM) on top of a software RAID. Tip: LVM itself supports logical volumes in RAID configurations. See LVM#RAID for an alternative to this article.How blocks of data in an LV are placed onto physical devices is determined by the RAID level. RAID levels are commonly referred to by number, e.g. raid1, raid5. Selecting a RAID level involves tradeoffs among physical device requirements, fault tolerance, and performance.When you create a RAID logical volume (LV), LVM creates a metadata subvolume that is one extent in size for every data or parity subvolume in the array. For example, creating a 2-way RAID1 array results in two metadata subvolumes (lv_rmeta_0 and lv_rmeta_1) and two data subvolumes (lv_rimage_0 and lv_rimage_1).
raid levels jbod
How LV data blocks are placed onto PVs is determined by the RAID level. RAID levels are commonly referred to as 'raid' followed by a number, e.g. raid1, raid5 or raid6. Selecting a RAID level involves making tradeoffs among: physical device . LVM supports Raid takeover, which means converting a RAID logical volume from one RAID level to another (such as from RAID 5 to RAID 6). Changing the RAID level is usually done to increase or decrease resilience to device failures or to restripe logical volumes. You use the lvconvert for RAID takeover.How LV data blocks are placed onto PVs is determined by the RAID level. RAID levels are commonly referred to as ’raid’ followed by a number, e.g. raid1, raid5 or raid6. Selecting a RAID level involves making tradeoffs among: physical device requirements, fault tolerance, and performance. A description of the RAID levels can be found at To create a RAID logical volume, you specify a raid type as the --type argument of the lvcreate command.
LVM RAID is a way to create a Logical Volume (LV) that uses multiple physical devices to improve performance or tolerate device failures. In LVM, the physical devices are Physical Volumes (PVs) in a single Volume Group (VG).There is a huge benefit in having LV based RAID. I do have a LV with RAID1 for more hard to reproduce data and normal LVs for the rest, this gives me maximum flexibility for size vs. redundancy considerations.
LVM RAID is a method to create a logical volume (LV) which uses several physical disks to improve performance or fault tolerance. Within LVM, physical disks (abbreviated as PV, physical volumes) belong to one volume group (VG).


raid levels explained

raid levels diagram
raid levels chart
raid explained for dummies
Gaujienā ''Egļukalna'' estrādē - Apes novads, Gaujienas pagastā, Latvia
lv raid|raid levels jbod